A plate and frame heat exchanger is a type of equipment used to transfer heat between two fluids. These heat exchangers are composed of a series of stainless-steel plates stacked and sealed with gaskets. The plates are designed to create a series of channels through which the fluids can flow, allowing for efficient heat transfer.
Advantages of Plate and Frame Heat Exchangers
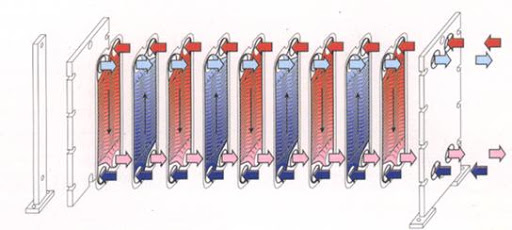
One of the main advantages of plate and frame heat exchangers is their high thermal efficiency. Because of the large surface area created by the stacked plates, plate and frame heat exchangers take up less space.
Another advantage of plate and frame heat exchangers is their flexibility. The plates can be removed and cleaned, making maintenance and repair a straightforward process. The plates can be replaced or reconfigured to accommodate changes in the fluid flow or heat transfer requirements.
Type of Plate and Frame Heat Exchangers
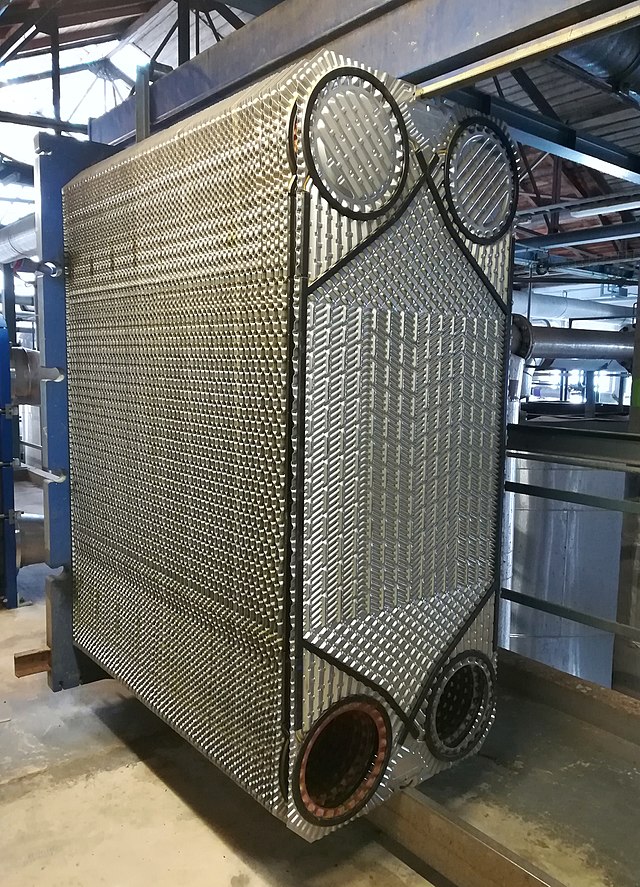


There are a few types of plate and frame heat exchangers, each designed for specific applications. The most common types are:
-Gasketed plate heat exchangers: use elastomeric gaskets to seal the plates together.
-Welded plate heat exchangers: The plates are welded together to form a sealed unit.
-Brazed plate heat exchangers: The plates are bonded together with a brazing alloy to form a sealed unit.
When choosing a plate and frame heat exchanger, it is important to consider the types of fluids being used. This includes their temperatures, pressures, and the amount of heat that needs to be transferred. The right heat exchanger will depend on the specific application and operating conditions.
Pressure Drop in Plate and Frame Heat Exchangers
A pressure drop in a plate and frame heat exchanger (PHE) can occur for several reasons. Some common causes include:
- Fouling. Over time, particles and other contaminants can accumulate on the plates of the heat exchanger, reducing their effectiveness and creating a pressure drop.
- Plate damage. Damaged or bent plates can disrupt the flow of fluid and create a pressure drop.
- Incorrect assembly. If the plates are assembled incorrectly the seal between the plates on’t be tight, resulting in a pressure drop.
- Clogging: If the fluid contains particles that can get stuck in the heat exchanger, it can clog the passages and create a pressure drop.
- Incorrect design. It may not be able to handle the flow rate or pressure of the fluid, resulting in a pressure drop.
- Inadequate fluid flow. It may not be able to maintain a consistent flow through the heat exchanger, resulting in a pressure drop.
- Worn or faulty pump. It may not be able to provide enough pressure to maintain the flow through the heat exchanger, resulting in a pressure drop.
It is important to monitor the pressure drop. This is an indication that the heat exchanger is working incorrectly and may need to be cleaned, repaired, or replaced. If a pressure drop is not addressed, it could cause reduced heat transfer efficiency, increase the running costs, and can damage the heat exchanger.
In Conclusion



