It’s important to understand how your boiler feedwater system functions, especially when trying to extend the useful life of your equipment. Low-quality boiler feedwater contains impurities and gases that can damage the whole system. This will lead to a reduction in efficiency and, even worse, boiler leaks or system leaks. In order to prevent this from happening, you must determine what impurities are in your raw water.
What Are Boiler Feedwater Impurities?


Pipe Burst Caused By The Insulating Effects Of Scale
Pure water is neutral in regard to taste, odor, and color. It is a powerful and practical means of transporting energy with its convenient boiling point and steam generation. But this type of water is expensive to generate. Raw water from a well or municipality contains impurities such as suspended solids, dissolved solids, and dissolved gases. There are many specific elements that affect the water within each category.
These impurities vary depending on the waters source. Water is a universal solvent and has a tendency towards picking up minerals that will interfere with boiler efficiency. Feedwater can contain the aforementioned impurities as well as industrial wastes, sediment, and microorganisms. In the Midwest, we most commonly find calcium, magnesium, and silica. All water absorbs gas from the surrounding atmosphere and should be deaerated, or in some cases, run through a good hot water return tank.
What Typically Makes Up A Feedwater System?
According to Samco, a feedwater system typically includes some type of:
- Filtration and ultrafiltration
- Ion exchange/softening
- Membrane processes such as reverse osmosis and nanofiltration
- Deaeration/degasification
- Coagulation/chemical precipitation
Why A Boiler Feedwater System Matters
Poor water treatment can affect your boiler operations in a number of ways. Let’s take them one at a time.


Corrosion caused by dissolved gases in boiler feedwater.
DISSOLVED GASES
Oxygen and CO2 even in trace amounts as low as 5 ppm (parts per million) will cause major corrosion damage over time. Dissolved oxygen will react with carbon steel throughout the feedwater piping, economizers, and boiler, causing oxygen pitting and eventually leaks. Take every opportunity for internal inspection of your boiler, economizer, and piping to look for internal corrosion of this type.
Dissolved CO2 can come from poorly deaerated water or as a byproduct of chemical reactions taking place inside your boiler. When this CO2 travels out of the boiler with the steam, it can make the condensate acidic. This acid condensate will corrode your steam piping while also adding iron to your boiler water.
[A boiler feedwater system is just one component of your boiler system. Download our Boiler Maintenance Checklists and Logs to ensure feedwater doesn’t alter your boiler’s performance.]
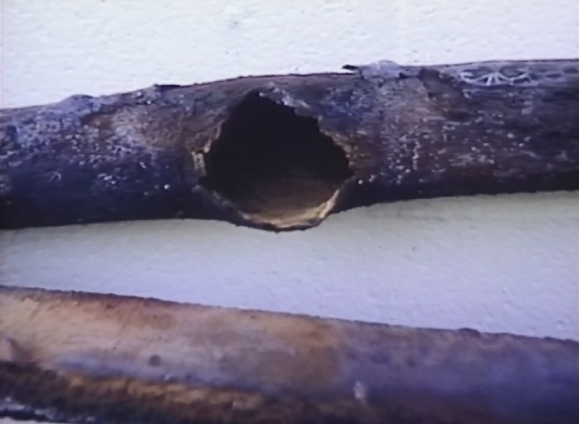
Dissolved Solids


Scale caused by calcium and magnesium in the water.
Dissolved solids such as calcium, magnesium, iron, and silica in feedwater can damage a boiler beyond repair. These dissolved solids come out of solution as the temperature of the water increases, forming a scale on nearby surfaces. Sometimes these scales form in feedwater pipe and economizers. In many cases, this scale is first seen in the boiler, where the heat transfer occurs. This scale prevents boiler water from cooling metal heat-absorbing surfaces, leading first to a loss of efficiency. This loss of efficiency can be noted by a steadily increasing boiler outlet temperature in the boiler operator’s logbook. As the problem worsens, the boiler will have a number of issues with uneven thermal growth, such as tube roll leaks. When the scale is so thick that it prevents the boiler water from cooling the heat transfer surfaces, the boiler tubes may completely fail.
Foaming Carry-Over
Foaming carry-over is a function of normal boiler impurities becoming too concentrated or over-treatment with chemicals. It can also be caused by an accidental introduction of organic matter (grease or oil) into the boiler feedwater or condensate return. The foam inside the boiler is easily forced out of the boiler steam outlet and can cause major damage. Water hammer in a steam line, erosion in steam piping, and boiler low water events are damaging to your system.
What Needs To Be Done About It?


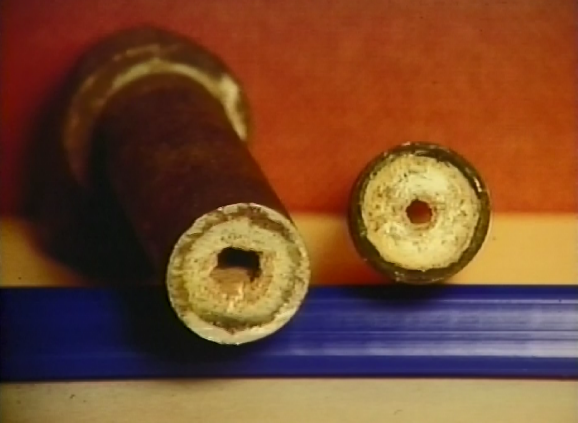
Corrosion caused by poor feedwater.
The good news is, that all these issues can be prevented with a good boiler feedwater system. Always preheat, deaerate, and chemically treat raw water to protect your boiler room equipment and the steam system in general. The most effective and lowest cost water treatment program goes in that order. Remove as much of the gas and impurities as possible mechanically, then treat the remaining traces with a good chemical treatment program.
HOW TO PREVENT DISSOLVED GASES ISSUES
Dissolved gases are mostly driven out of feedwater in the Deaerator or hot water tank. The proper function of these systems is essential to preventing corrosion both in the boiler room and in the steam system. Careful attention is required to ensure that gases can be removed from the boiler water prior to feeding the boiler. Good practice would be to record the feedwater temperature in your boiler logbook during every operator round.
Note: A high function boiler feedwater system consists of more than a deaerator hot water tank. A good chemical treatment program removes the remaining trace amounts of dissolved gas.
- If your feedwater temperature drops (below 190 F for hot water tanks or below 225 F for deaerators), contact us right away. You want to diagnose the problem before it can damage your boiler and steam system.
HOW TO PREVENT DISSOLVED SOLIDS ISSUES
You can remove dissolved solids, depending on the nature of the impurity, in a variety of ways. In the Midwest, typical water treatment requires a water softener at a minimum to remove the Calcium and magnesium. Many systems also include RO Systems (Reverse Osmosis) to remove calcium, Magnesium, and Silica in addition to the softener. A good water treatment company can measure the impurities in your raw water, as well as in your feedwater. They can then make recommendations for improving your water treatment and provide you with chemical treatment recommendations. Good practice would be to record water conductivity in your boiler logbook during every operator round. Be sure to include makeup water conductivity, feedwater conductivity, and boiler water conductivity.


Embrittlement of a boiler tube causing a crack due to poor water treatment.
- When your makeup water conductivity is above the recommendation of your water treatment company, you need to begin troubleshooting your raw water treatment. If the problems persist, contact a qualified service company to troubleshoot the system.
- When boiler water conductivity is above the recommendation of your water treatment company, you are likely forming a scale on heat transfer surfaces! Perform a good blowdown to get conductivity within range, and adjust your continuous blowdown accordingly to prevent future upsets. Be sure to call your water chemical company for “best practice” advice on adjusting blowdown.
HOW TO PREVENT FOAMING CARRY-OVER
If you suspect carry-over or foaming, immediately verify your boiler water conductivity is within range. If it is, call your water treatment company to help identify the cause of the foaming. They can perform a number of tests on the feedwater, boiler water, and condensate to confirm a carry-over situation. In some cases, you need to bring the boiler offline and have a thorough cleaning done by a qualified service company. This will allow them to clean the oil, grease or other product contamination effectively. In other cases, you can address the foaming with a simple water additive.

- If carry-over is caused ‘mechanically’ or by the way the boiler is being loaded, contact Rasmussen Mechanical Services to help diagnose the root cause.
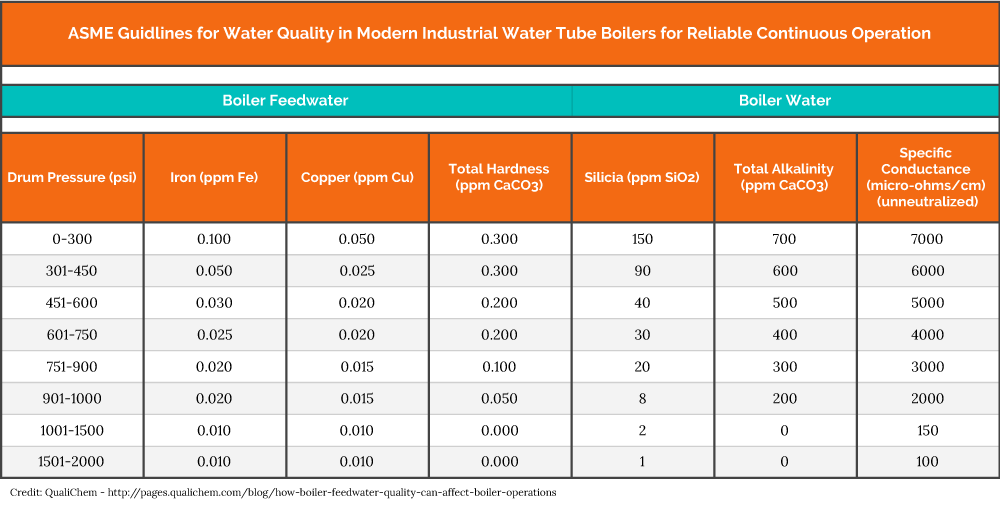
When you need to generate steam, it can be frustrating to have a simple process impeded by outside variables. These impurities can clog strainers and valves, cause pipe or tube failures or form sludge build-up and corrosion within the boiler system. Each boiler system has its own limit of Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) in the feedwater and the boiler. Set this limit with a water chemistry supplier. You will need to take into consideration your water, your plant, and the chemical program in use. Use the chart below as a reference for some general guidelines. However, your water chemistry supplier will help you set better guidelines based on the chemistry you are using and the impurities in your water.

Get Your Free Spare Parts List
Boiler Feedwater System Summary
In summary, pre-treatment of boiler feedwater can make all the difference when trying to prevent costly shutdowns and extensive boiler maintenance. Starting with good water keeps your system flowing efficiently and prevents system damage. Removing impurities is a necessary step for any boiler process, but it is only one part of the process. Rasmussen Mechanical Services works with your boiler operators and your water treatment company to keep your system running efficiently and reliably.
If you have any questions about boiler feedwater systems or want a second opinion, drop us a line. The Rasmussen Mechanical Services Team is at your service. Save your boiler and save yourself the headache of future complications today.