Before we jump into our Air Compressor Maintenance Checklist, lets first look at an energy saving study performed by the U.S. Department of Energy:
“An air system that serves a 100-horsepower (hp) compressor operating continuously at a cost of $0.08/kWh has annual energy costs of $63,232. With a dirty coalescing filter, the pressure drop across the filter could increase to as much as 6 psi, vs. 2 psi when clean. The pressure drop of 4 psi accounts for 2% of the system’s annual compressed air energy costs. (oran increase of $1,265 per year)”
Neglecting even just one component of your compressed air system can cost you a significant amount of money. Routine maintenance is critical to ensure a compressed air system remains reliable, safe and efficient. As always, follow your manufacturer’s recommendations for routine maintenance and maintain a Compressed Air log book.
Air Compressor Maintenance Checklist
- Visually Inspect Air Compressor
- Check and Log Drive Motor Bearing Temps
- Check and Log Fan Motor Bearing Temps
- Inspect Coupler, Hub and Shaft Seal
- Check and Log Oil Cooler Temps
- Check and Log After Cooler Temps
- Inspect Scavenge Line Check Valve
- Check Drive Belt condition if applicable
- Log load and unload pressure settings
- Check moisture trap or autodrain
- Perform An Oil Sample Analysis
- Change Oil Filter
- Blow Out Coolers
- Change Air Filter
- Change Oil/Water Separator
- Check and log ambient condition
- Change Oil Separator O-Ring if necessary
- Change Oil if necessary
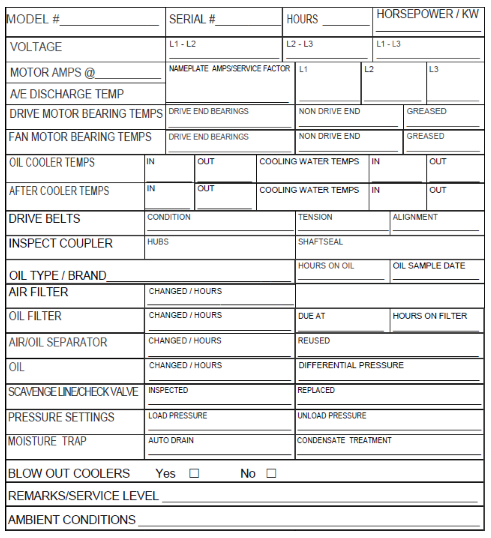
Air Compressed Maintenance Logs
Download our Air Compressor Logs Sheet for a simple easy to use format.
What should be included in air compressor maintenance logs? Below, is a list to help get you started. These are items that are important to monitor and gauge in an effective maintenance strategy.
- Name of who performed service:
- Model #
- Serial #
- Hours
- Horse Power
- Motor Amps @
- Nameplate Amps
- A/E Discharge Temp
- Drive motor bearing temps (Drive end bearings / non-drive end bearings)
- Fan Motor Bearing Temps (Drive end bearings / non-drive end bearings)
- Oil Cooler Temps (In and Out) / Cooling water Temps (In and Out)
- After Cooler Temps (In and Out) / Cooling water Temps (In and Out)
- Drive Belt Condition, Tension and Alignment
- Inspect Coupler (Hubs and Shaft seal)
- Oil Type/ Brand
- Hours On Oil and Oil Sample Date
- Air Filter Changed Date / Hours
- Oil Filter Changed Date / Due Date / Hours On Filter
- Air/Oil Separator (Changed / Hours and if reused or replaced)
- Oil Differential Pressure
- Scavenge Line / Check Valve (Inspected / Replaced)
- Pressure Settings (Load Pressure / Unload Pressure)
- Moisture Trap (auto Drain / Condensate treatment)
- Blow Out Coolers (Yes / No)
- Remarks
- Ambient Conditions
Finding and Fixing Air Compressor Leaks
Another crucial aspect of preventative maintenance involves finding and addressing leaks early. Compressed air leaks can be financially crippling under the wrong circumstances. The most terrifying aspect of compressed air leaks is just how long they can go undetected. According to the Compressed Air & Gas Institute, a single ¼-inch leak in a compressed air line can cost a facility anywhere from
$2,500 to $8,000/yr. The scary part is, you may not even know it.
A simple walkthrough with a pair of good ears may detect some major leaks. You also might be able to notice a change in equipment productivity. However, if you can detect issues this way, the problem has already become very costly.
To reliably identify compressed air leaks, especially in loud environments, deploy specialized equipment and a skilled technician. Ultrasonic leak detection devices are the best tool to recognize compressed air leaks. Their regular use can help maintain consistent and high functionality of a compressed air system. Regular leak audits reduce wasted energy expenses, unnecessary wear on air compressors and help prevent air compressor downtime.
COST ($/YEAR) = MOTOR BHP X .746 X HOURS OF OPERATION (PER YEAR) X ELECTRIC RATE ($/KWH) / MOTOR EFFICIENCY
If you are unsure how much money your compressed air system uses, try using this equation from the Compressed Air & Gas Institute:
Common Location for Leaks
Leaks most commonly occur at the following locations:
- Couplings
- Hoses
- Tubes
- Fittings
- Pipe Joints
- Quick Disconnects
- FRLs (filter, regulator, lubricator)
- Condensate Traps
- Valves
- Flanges
- Packing
- Thread Sealant
- Point-Of-Use Devices
Download the Air Compressor Maintenance Checklist PDF for an easy-to-use checklist, formatted to make maintenance tasks easily accounted for.
Need Help?
Looking for commercial air compressor services, sales or support? Reach out to one of our offices in Omaha, Council Bluffs, Denver, Sioux City, Sturgis, Gibbon or Lincoln.
What are you waiting for? Contact the experts at Rasmussen Mechanical Services to ensure they properly maintain your air compressor. Call us at 1-800-237-3141, email sales@rasmech.com, chat with a support agent, or contact us online.