Boilers are an essential part of many industries, providing heat and power to a wide range of processes. While they are typically very safe, there are still some risks associated with operating boilers, particularly when it comes to pressure buildup. To mitigate these risks, it’s important to have safety relief valves installed on your boiler.

Picture Courtesy Of invenoeng.com
What Are Safety Relief Valves?
A safety relief valve is a critical safety component in boilers that helps regulate pressure levels in the system. It is designed to open and release excess pressure when the pressure within the system exceeds a certain threshold. This prevents damage to the boiler and other components, as well as potential explosions. The safety relief valve ensures that the boiler operates within safe pressure limits, providing a safer work environment for employees.
Types of Safety Relief Valves
There are a number of different types of safety valves available, two common ones include spring-loaded valves and pilot-operated valves. Spring-loaded valves are the most common type of safety relief valve. They are designed to open when the pressure in the system exceeds a set pressure level. Pilot-operated valves are suitable for high-pressure applications and are also used on vessels. These valves offer precise pressure control and offer large relieving capacities.
Choosing The Right Safety Relief Valve
When it comes to choosing the right valve, there are several factors to consider. These factors include the type of boiler, pressure and temperature ratings, and the specific requirements of your industry. Here are some key considerations to keep in mind when selecting a safety relief valve:

- Type of Boiler: The type of boiler will influence the type of valve you need. For instance, high-pressure boilers require different types of relief valves than low-pressure boilers.
- Pressure and Temperature Ratings: The pressure and temperature ratings of the relief valve should match those of the boiler. Safety valves are designed to open at a specific pressure. This is why it is essential to select a valve that matches the pressure rating of your system.
- Valve Size: The size of the safety relief valve is an important consideration. The valve must be large enough to handle the volume of steam or hot water produced by the boiler.
- Material: The material used to manufacture the valve should be compatible with the material used in the boiler. This is important to prevent corrosion and ensure the longevity of the valve.
- Industry Requirements: Some industries have specific requirements, such as certifications or compliance with specific standards. Be sure to check any industry-specific requirements before selecting a valve.
- Installation and Maintenance: Consider the ease of installation and maintenance. It should be easy to install, and maintenance should be straightforward and not require specialized equipment.
Safety Valve Installation Considerations

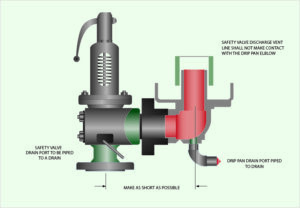
Spirax Sarco does a good job explaining one of the key considerations while installing a safety valve. “Seat damage can often occur when a valve is first lifted as part of the general plant commissioning procedure. This is because very often, dirt and debris are present in the system. To ensure that foreign matter does not pass through the valve, the system should be flushed out before the safety valve is installed. The valve must be mounted where dirt, scale and debris cannot collect.
It is also important, on steam applications, to reduce the propensity for leakage. Do this by installing the valve so that condensate cannot collect on the upstream side of the disc. This can be achieved by installing the safety valve above the steam pipe”
Mounting Valves
Allied Valve Inc suggests 4 considerations when mounting a safety valve.
- Mount PRVs in a vertical position, which means upright and with the spindle vertical. A valve installed in any position other than vertical might perform incorrectly.
- For flanged valves, be sure to draw the bolts down evenly. This is especially crucial for cast iron valves. If you tighten one side all of the way and then the other, you won’t be able to tighten it completely. This could result in a crack in the valve.
- Avoid overtightening the valve. This can damage both the inlet and the outlet threads and cause leakage.
- Apply pipe dope to the male threads only. Pipe dope is a compound that prevents valves from leaking, but if you apply it to the female threads, it could contaminate your system.
Rebuilding Safety Valves
There are 3 things you can do to recertify a safety valve, typically done annually. You can have it replaced, tested or rebuilt. Replacement is self explanatory. Testing involves ensuring the valve lifts at a certain PSI and that it does not leak. Rebuilding a safety relief valve involves disassembling the valve, inspecting its parts, and replacing any damaged components. Only an ASME certified valve shop can test or rebuild a safety valve. Here are the general steps for rebuilding a safety relief valve:
- Clean the parts: The valve is disassembled into all of its components. All parts of the valve are cleaned with a suitable cleaning agent to remove any dirt, debris, or rust.
- Inspect the parts: Inspect all parts of the valve, including the disc, seat, spring, and stem, for any damage or wear. Measurements are also taken to ensure the valve meets the manufactures requirements.
- Replace damaged parts: Replace any damaged or worn parts with new ones. Make sure to use genuine replacement parts recommended by the valve manufacturer.
- Reassemble the valve: Reassemble the valve according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Make sure to lubricate all moving parts with a suitable lubricant.
- Test the valve: Test the valve to ensure it is functioning properly. You can use a test bench or install the valve back into the system and test it under normal operating conditions.
- Record the rebuild: Record the rebuild in the valve’s maintenance log and tag the valve. This including the date, parts replaced, and test results. This helps to ensure that the valve is properly maintained and that you have a record of its service history.
Valve Maintenance
To ensure the valve operates correctly, it should be inspected at least once a year and tested to ensure it is functioning correctly. During the inspection, the valve should be checked for leaks, corrosion, and other signs of wear and tear. If any issues are detected, the valve should be replaced immediately.
Additionally, these valves should not be tampered with or adjusted by untrained personnel. Any adjustments or repairs should be carried out by a certified valve repair shop who understands the safety risks and code rules associated.
Safety Relief Valve FAQ’s
- What are the 3 main types of safety relief valves? The three main types of safety valves are spring-loaded safety valves, pilot-operated relief valves, and balanced bellows relief valves.
- How do I choose a safety valve? Factors such as the type of fluid, pressure, temperature, flow rate, and the required discharge capacity must be considered. Additionally, relevant codes and regulations should be consulted to ensure compliance.
- How do I know what size valve I need? The size of the valve is determined by the maximum flow rate, the set pressure, and the specific gravity of the fluid being discharged. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code provides guidelines for sizing pressure relief valves based on these factors.
- Where should a safety valve be located? A safety relief valve should be located on the highest part of the boiler, and before any steam control valves or other obstructions.
- What’s the difference between low-lift valves and a full-lift valves? “Low lift safety valve – The actual position of the disc determines the discharge area of the valve. Full lift safety valve – The discharge area is not determined by the position of the disc.” – according to Spirax Sarco.
Their Importance For Boilers

First, they help to prevent catastrophic accidents. If a boiler were to experience a sudden increase in pressure, it could rupture or explode. They provide a last line of defense against such disasters, helping to prevent pressure buildup and allowing the boiler to operate safely.
Another important reason safety valves are important is that they can help to prevent damage to the boiler itself. When pressure builds up in a boiler, it can cause a variety of mechanical failures, including cracks, leaks, and ruptures. By providing a way for excess pressure to escape, these valves can help to protect the boiler from these kinds of damage.
Finally, these valves are required by law and industry standards. Many local and national regulations mandate that boilers must have safety relief valves installed. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in fines or other penalties.
In Summary
Safety relief valves are critical components in boilers that regulate pressure levels in the system, preventing damage to the boiler and other components as well as potential explosions. There are different types of safety relief valves available, including spring-loaded valves, bellows valves, and pilot-operated valves, each with specific applications. Choosing the right valve depends on several factors, including the type of boiler, pressure and temperature ratings, valve size, material, industry requirements, installation, and maintenance. To ensure the valve operates correctly, it should be inspected at least once a year and tested to ensure it is functioning correctly. Safety relief valves should be mounted in a vertical position and in a location that prevents the collection of dirt and debris. Valve maintenance should only be carried out by qualified personnel.


